In today’s guide we will cover how to install Drupal 9 CMS on CentOS 8 Linux system. Drupal is an open source content management system that enables content creators to build amazing digital experience. With Drupal it becomes easy to create a new website and add, edit, publish, or remove content all on a web browser. The Drupal software is written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License.
Most of the features of Drupal 9 came from the improvements of Drupal 8 and new additional features. Some features of Drupal CMS are:
- Layout Builder: Allows content editors to design pages without engineering help
- API-first architecture: Enables building robust decoupled and headless applications
- Media Library: Makes the management of images, video, and other assets easier than ever before.
- Automated updates
- New admin interface and default theme
How To Install Drupal 9 CMS on CentOS 8
Before you start the installation of Drupal 9 CMS on CentOS 8 take note of below new requirements.
- PHP >=7.3
- MySQL or Percona, version >=5.7.8
- MariaDB >=10.3.7
- PostgreSQL >=10
If you follow below steps keenly you should have a working Drupal 9 CMS installed on your CentOS 8 server.
Step 1: Update System
Ensure your system is updated to the latest release:
sudo dnf -y update && sudo systemctl rebootOnce the server has come up login again and confirm updates were applied.
$ ssh username@serveripStep 2: Install MariaDB database on CentOS 8
There are many databases that can be used by Drupal. My database of choice is MariaDB.
Run these commands to install MariaDB database server on CentOS 8 Linux.
sudo dnf -y install @mariadbStart and enable the service after installation.
sudo systemctl enable --now mariadbConfirm the service is in running state:
$ systemctl status mariadb
● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.3 database server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2020-06-27 00:59:27 CEST; 33s ago
Docs: man:mysqld(8)
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/
Process: 3945 ExecStartPost=/usr/libexec/mysql-check-upgrade (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3811 ExecStartPre=/usr/libexec/mysql-prepare-db-dir mariadb.service (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3786 ExecStartPre=/usr/libexec/mysql-check-socket (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3913 (mysqld)
Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..."
Tasks: 30 (limit: 24403)
Memory: 85.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service
└─3913 /usr/libexec/mysqld --basedir=/usr
......Secure your database server by setting root password, disabling root remote logins and removing test databases that we don’t need.
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!Test that you can login to database as root user with password set
$ mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 16
Server version: 10.3.17-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> Step 3: Create Drupal Database
A database and user is required by Drupal CMS to be functional. Open MariaDB shell.
$ mysql -u root -pCreate database and user for Drupal.
CREATE DATABASE drupal;
GRANT ALL ON drupal.* TO 'drupal'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Str0ngDrupaLP@SS';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
\q
Step 4: Install PHP 7.3 and Apache Web Server
Install PHP on CentOS 8 Linux:
sudo dnf module disable php:7.2
sudo dnf module enable php:7.3
sudo dnf -y install php php-{cli,fpm,gd,mysqlnd,mbstring,json,common,dba,dbg,devel,embedded,enchant,bcmath,gmp,intl,ldap,odbc,pdo,opcache,pear,pgsql,process,recode,snmp,soap,xml,xmlrpc}Confirm PHP version:
$ php -v
PHP 7.3.5 (cli) (built: Apr 30 2019 08:37:17) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) 1997-2018 The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.3.5, Copyright (c) 1998-2018 Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v7.3.5, Copyright (c) 1999-2018, by Zend TechnologiesInstall Apache web server.
sudo dnf -y install httpdSet PHP Timezone and memory limit.
$ sudo vim /etc/php.ini
memory_limit = 256M
date.timezone = Africa/NairobiStart both httpd and php-fpm services.
sudo systemctl enable --now httpd php-fpmCheck if services are running:
$ systemctl status httpd php-fpm
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.d
└─php-fpm.conf
Active: active (running) since Sat 2020-06-27 01:08:32 CEST; 1min 38s ago
Docs: man:httpd.service(8)
Main PID: 5317 (httpd)
Status: "Running, listening on: port 80"
Tasks: 213 (limit: 24403)
Memory: 25.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
├─5317 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─5319 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─5320 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─5321 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
└─5322 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
Jun 27 01:08:32 centos.computingforgeeks.com systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
Jun 27 01:08:32 centos.computingforgeeks.com systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
Jun 27 01:08:32 centos.computingforgeeks.com httpd[5317]: Server configured, listening on: port 80
● php-fpm.service - The PHP FastCGI Process Manager
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2020-06-27 01:08:32 CEST; 1min 38s ago
Main PID: 5318 (php-fpm)
Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 5, Requests: 0, slow: 0, Traffic: 0req/sec"
Tasks: 6 (limit: 24403)
Memory: 36.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/php-fpm.service
├─5318 php-fpm: master process (/etc/php-fpm.conf)
├─5534 php-fpm: pool www
├─5535 php-fpm: pool www
├─5536 php-fpm: pool www
├─5537 php-fpm: pool www
└─5538 php-fpm: pool www
Jun 27 01:08:32 centos.computingforgeeks.com systemd[1]: Starting The PHP FastCGI Process Manager...
Jun 27 01:08:32 centos.computingforgeeks.com systemd[1]: Started The PHP FastCGI Process Manager.If you have firewalld service running open port 80 and 443 for SSL:
sudo firewall-cmd --add-service={http,https} --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadStep 5: Download Drupal 9 on CentOS 8
Download the Drupal 9 tarball to the host where the service will run.
sudo dnf install -y wget
wget https://www.drupal.org/download-latest/tar.gz -O drupal.tar.gzExtract downloaded file.
tar xvf drupal.tar.gzMove resulting folder to /var/www/html directory.
rm -f drupal*.tar.gz
sudo mv drupal-*/ /var/www/html/drupalConfirm file contents:
$ ls /var/www/html/drupal
autoload.php core INSTALL.txt profiles sites vendor
composer.json example.gitignore LICENSE.txt README.txt themes web.config
composer.lock index.php modules robots.txt update.phpSet ownership of drupal directory to Apache user and group.
sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/Create additional directories and files required by Drupal installer.
sudo mkdir /var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/files
sudo cp /var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/default.settings.php /var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/settings.phpFix SELinux Labels:
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/drupal(/.*)?"
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/settings.php'
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/files'
sudo restorecon -Rv /var/www/html/drupal
sudo restorecon -v /var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/settings.php
sudo restorecon -Rv /var/www/html/drupal/sites/default/files
sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/drupalStep 6: Configure Apache for Drupal
Create a new Apache configuration for Drupal website.
sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/drupal.confModify below content and add to file – set domain, admin user and correct path to Drupal data.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName mysite.com
ServerAlias www.mysite.com
ServerAdmin admin@mysite.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/drupal/
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/access_log combined
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/error_log
<Directory /var/www/html/drupal>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
RewriteEngine on
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?q=$1 [L,QSA]
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>Confirm configuration syntax:
$ sudo apachectl -t
Syntax OKRestart web server.
systemctl restart httpdStep 7: Install Drupal 9 on CentOS 8
In your web browser open the Server DNS name to finish the installation of Drupal 9 on CentOS 8.
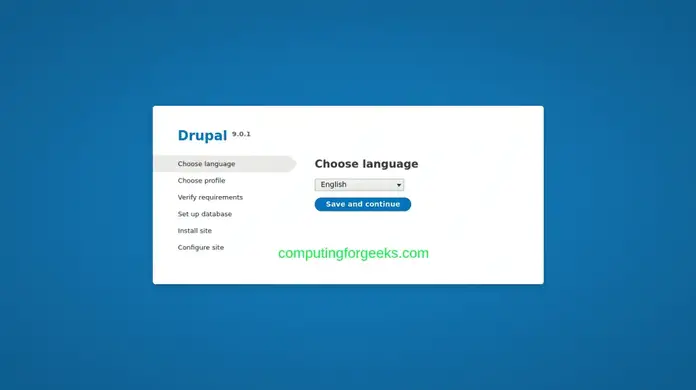
Choose Language:
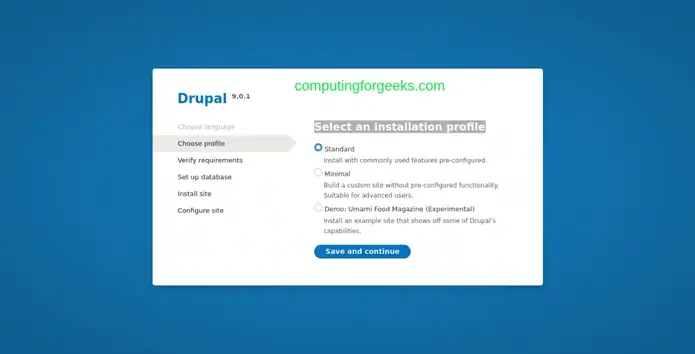
Select an installation profile:
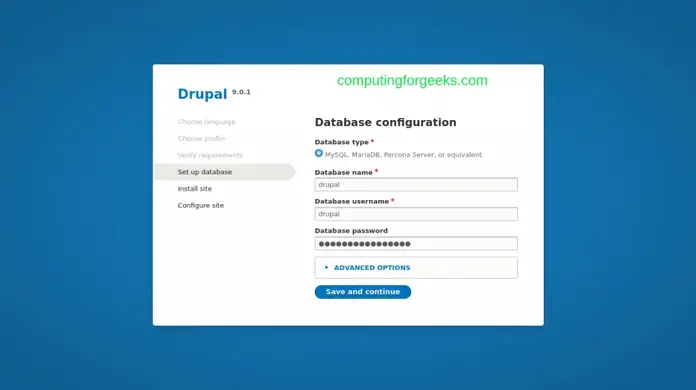
Configure Database for Drupal:
Drupal installation is started. Wait for it to complete:
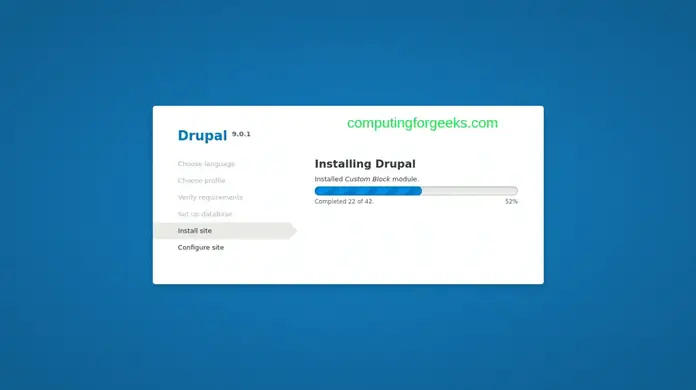
Configure your site:
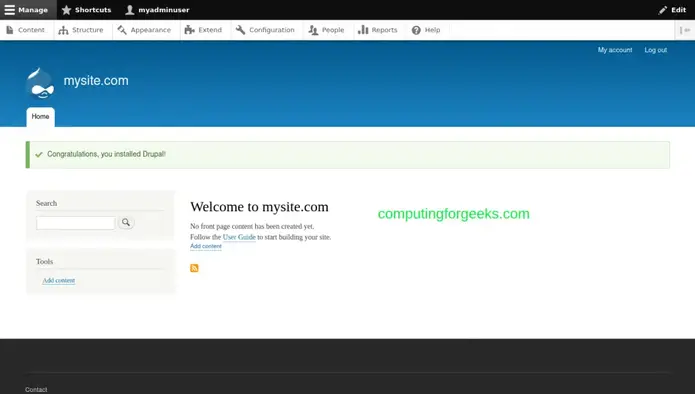
You have successfully installed Drupal 9 on a CentOS 8 server. Refer to the official documentation for more tuning and advanced configurations.